Defining a Database Connection
The Real-Time Designer supports two types of database connections:
Local connection: Each agent has its own direct connection to the database.
Server connection: A single connection is made to the database, which is used by all agents to obtain data from the connected database. This type of connection is advantageous when a large number of agents need to be connected to the database at the same time. Because there is only one connection to the database, the maximum number of network connections allowed is not reached or exceeded.
The sample connection string as given below:
SQL: jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://server: 49423/db;user=userName;password=password Jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://1.9.52.30:1433/ISE_QA_MAIN;username=rti_generic_user;password=rti_generic_user
To define a local database connection:
| 1. | Open the Database Element window (see Defining Database Objects). |
| 2. | On the ribbon, click Add New Connection and then select Add Local Connection to display a new Local Connection branch in the Data Connections tree. |
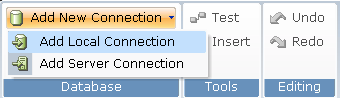
The new branch is selected and the Connection tab opens in the main work area.
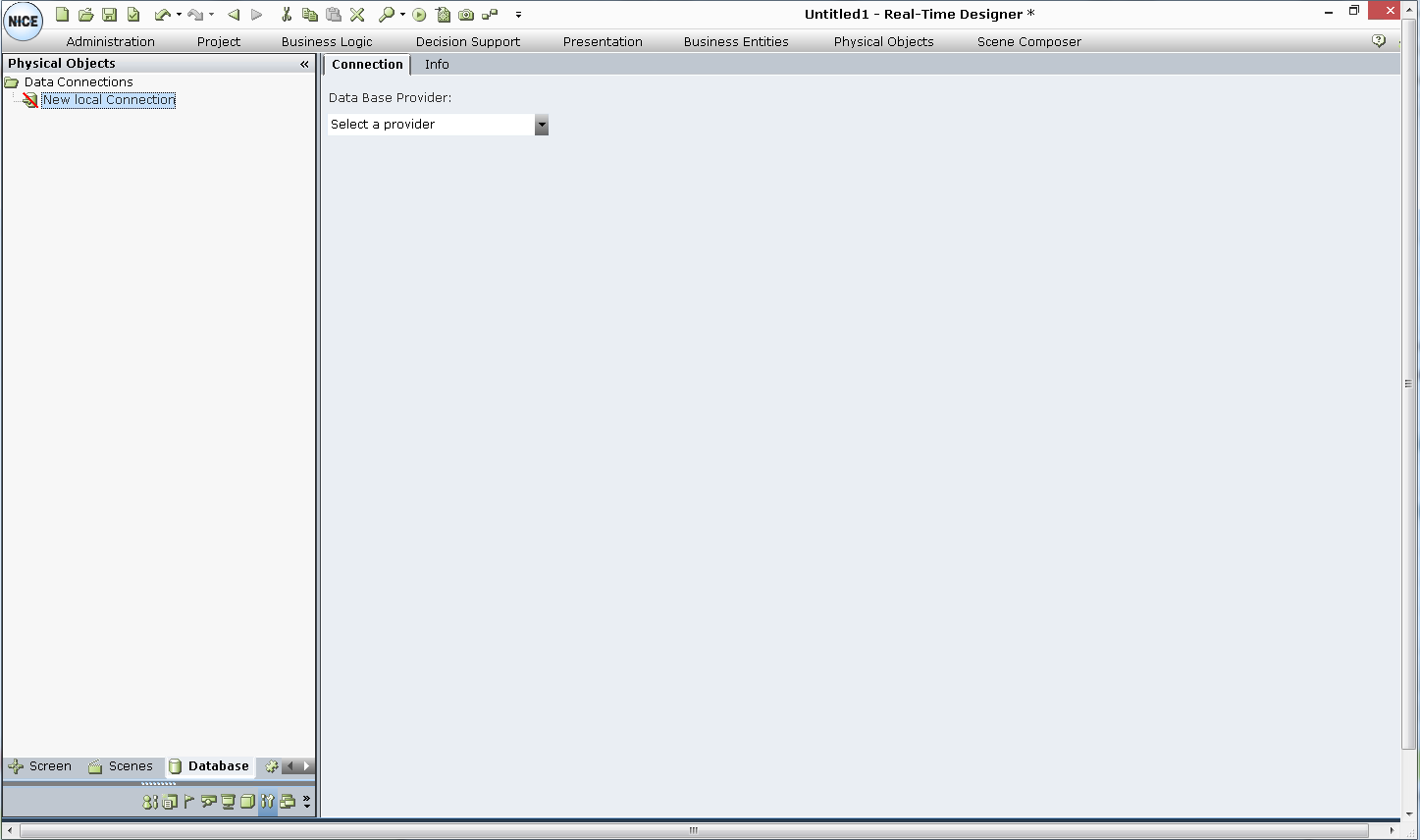
| 3. | A provider specifies the driver that enables the connection to the database. From the Select a provider drop-down list, select a provider. |
| 4. | Define the specific database connection parameters required by the selected provider. These parameters are standard connection parameters to each database and differ for each database type. Microsoft Access Database Engine installation must be 32-bit. |
Microsoft Access Connection (includes Microsoft Access 2007, in addition to Microsoft Access MDB (2003)
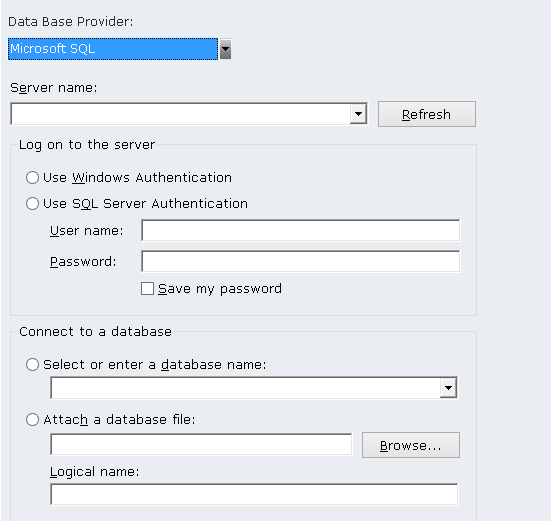
Microsoft SQL Connection
ODBC Connection - To establish connection with Snowflake DB, see Connecting to Snowflake Database.
OleDB Connection
Oracle Connection - To establish connection with Oracle DB, see Creating Oracle DB Connection.
The following window shows an example for a Microsoft SQL connection:
| 5. | Whenever you create a new database connection, you must test it. On the ribbon, click Test to test the connection to the database and validate this database element in Real-Time Designer. |
 : Indicates a successful connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
: Indicates a successful connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
 : Indicates that there is no connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
: Indicates that there is no connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
To define a server database connection:
RTServer includes a configuration for DB connectivity execution – Using binding variables (accessible from the RTServer Configuration Management console > Database section). When the value is True, executing the queries with dynamic table and column names is not supported.
A query through the Real-Time server will return only up to 50K records.
| 1. | Open the Database Element window (see Defining Database Objects). |
| 2. | On the ribbon, click Add New Connection, then select Add Server Connection to display a new Server Connection branch in the Data Connections tree. |
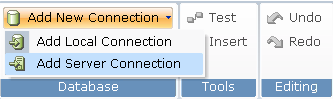
The new branch is selected and the main area on the right shows the Server DB Map option. This option specifies the server database connection mapping value to be used to connect to the database:
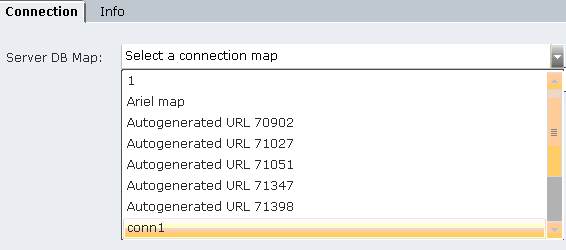
Select the applicable database connection mapping entry in the drop-down list. The values in this drop-down represent the values defined in the Name column for database connection mapping entries. These mapping entries are defined in the Server DB Connection Mapping branch in the Administration module, as described on in the System Administration Guide.
Connection strings vary, depending on the type of database being connected and the access privileges associated with the connection.
| 3. | Add commands to this database connection, such as INSERT, SELECT and DELETE commands. To add a command, right-click the connection in the Data Connections tree and select Add > New Server Command: |
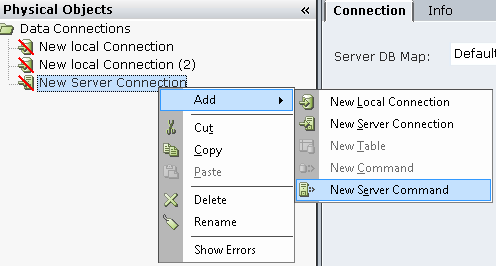
Commands are database-specific and differ for each database type. Each command that you add is added as a new sub-branch in the tree.
| 4. | On the ribbon, click Test to test the connection to the database and to validate this database element in Real-Time Designer. |
Whenever you create a new database connection or a new command, you must test it to make it valid. These objects are not valid until tested.
 : Indicates a successful connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
: Indicates a successful connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
 : Indicates that there is no connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
: Indicates that there is no connection between Real-Time Designer and the database.
Using Database Command Tables
A server database connection can be selected as an object in a rule's action or in other Action Editors, such as for a business entity function. These database connections have specific functionality that must be configured when defining the rule.
To be able to use Server Database Connection commands when executing Real-Time Designer in Test mode (by clicking the Play button), you must first deploy the solution using the Publish option. For further details, see Monitoring Services.
button), you must first deploy the solution using the Publish option. For further details, see Monitoring Services.
Using a Local Database Command
To use a local database command in an Action Editor:
| 1. | Select Data Connections in the Action Editor: |
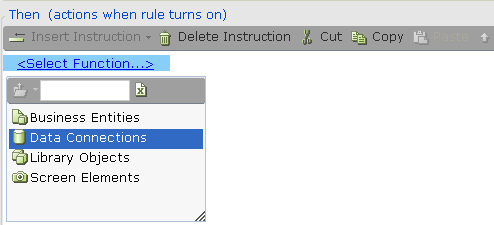
| 2. | Select the specific database connection: |
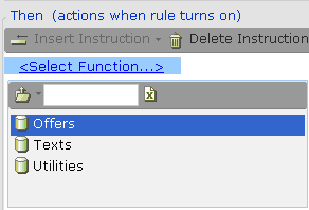
| 3. | Select the specific database command: |
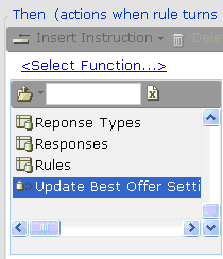
| 4. | Select the required function from the list of functions that can be performed for the command: |
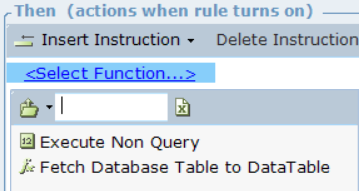
The available functions are:
Execute Non Query: This function executes a Transact-SQL statement against the connection. This function does not return a result set. Use it for commands that do not return values, such as INSERT and UPDATE commands. This function returns the number of affected rows.
Fetch Database Table to DataTable: This function returns the query result from the database to the datatable. The supported datatype in DataTable are boolean, datetime, decimal, number, and string. No parameter is required to invoke this function.
The following window is displayed:
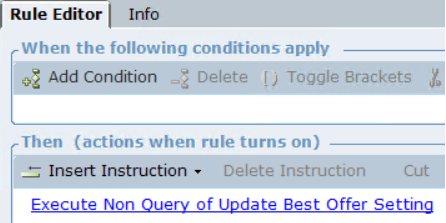
Using a Local Database Table
To use a local database table in an Action Editor:
| 1. | Select Data Connections in the Action Editor: |
| 2. | Select the specific database connection: |
| 3. | Select the required database table: |
| 4. | Select the required function from the list of functions that can be performed for the command: |
The available functions are:
Load for Update: This function enables you to later invoke an Update function that flushes updates made in memory to a business entity back to the database. For a local database connection, a query's result set is saved in memory. Updates can be made in memory that affect a business entity, and later flushed to the actual database, as a means to update the database.
The Load for Update function works in Asynchronous mode. For details, see page 1.
Consider an example where you want to use a table object to fill in the values in a business entity list. First, select Business Entities from the drop-down list:
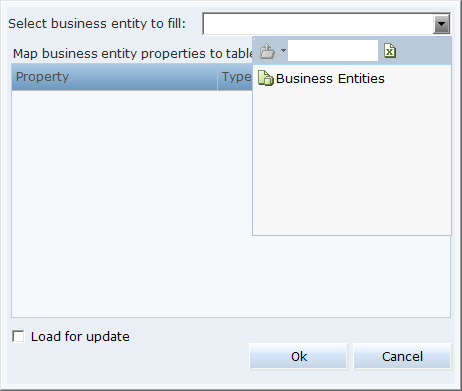
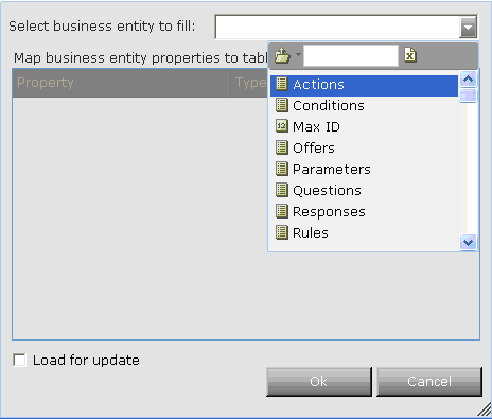
Next, drill down to select a specific business entity property. You can select either a single business entity instance or a business entity list, depending on what the query is designed to retrieve:
A window is displayed that shows the mapping of business entity properties to table columns (based on the table you selected above). If the result set for the query consists of more than one record, then the first record in the result set is assigned. For example:
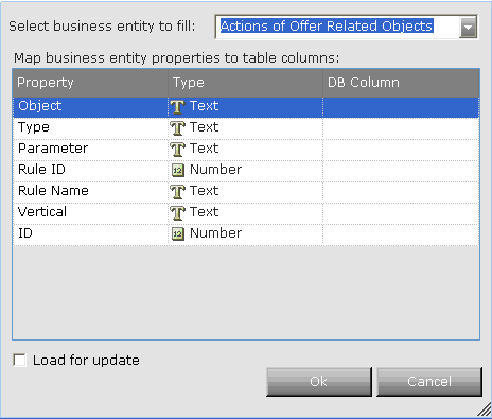
Each row in this window maps a property of the business entity type to a database column. You must map each row in this window before proceeding.
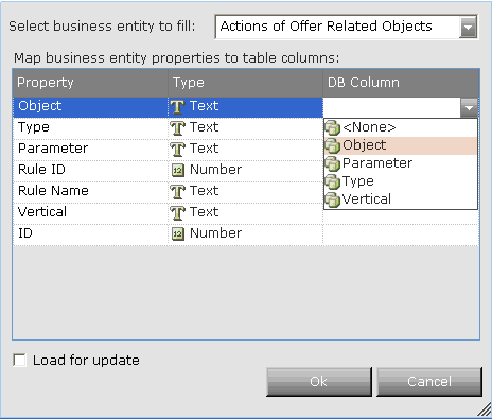
The mapping options that are displayed in the DB Column are for the type of property represented in that row. The figure above shows the available options for a text-type property. The figure below shows the available options for a numeric type property.
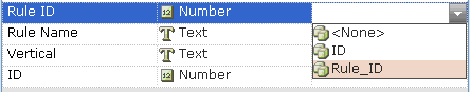
Select Load for update if you want to be able to invoke the Update function at a later time (see below).
Update: This function enables you to update the database with any changes made regarding the business entity in focus.
To update the database, it must have a primary key column. Databases that do not have a primary key column (for example, an Excel database), cannot be updated using this function.
Using function invocation, navigate to the data connection you want to update:
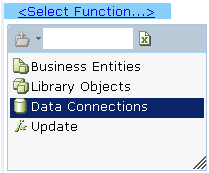
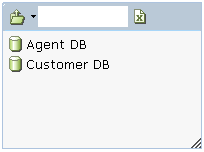
Select the database, and then choose the database table to update:
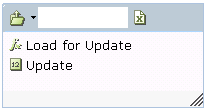
Next, select the Update function:
Select Business Entities to access the business entity that contains the values to be updated in the database tables:
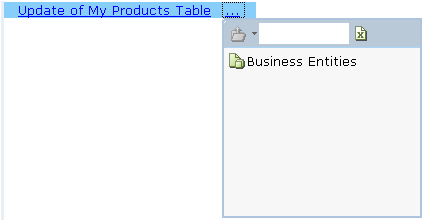
Then, select the specific business entity that contains the actual values to be updated in the database:
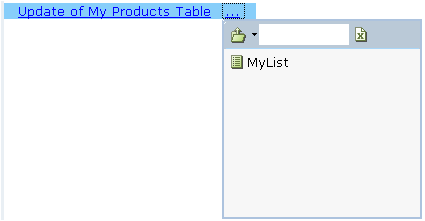
Using a Server Database Command
To use a server database command in an Action Editor:
| 1. | Select Data Connections in the Action Editor: |
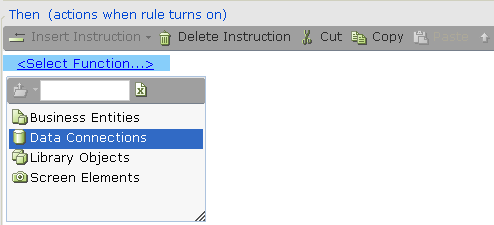
| 2. | Select the specific database connection: |
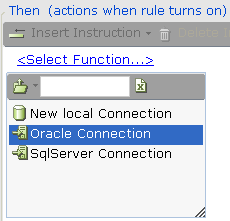
| 3. | Select the specific database command: |
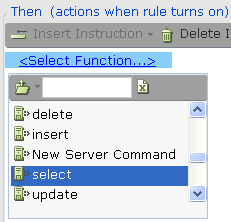
| 4. | Select the required function from the list of functions that can be performed for the command: |
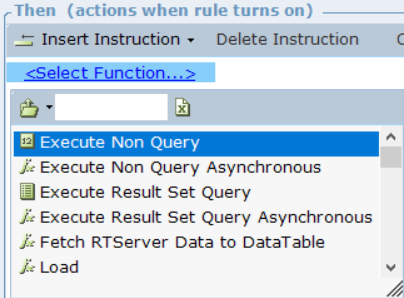
Each of these functions can be used in Asynchronous mode.
Execute Non Query: This function executes a Transact-SQL statement against the connection. This function does not return a result set. Use it for commands that do not return values, such as INSERT and UPDATE commands. This function returns the number of affected rows.
Execute Result Set Query: This function returns a list of rows. Each row contains a list of cells, which are the fields that comprise that row. The value of each cell is returned as a string, as shown in the following example:
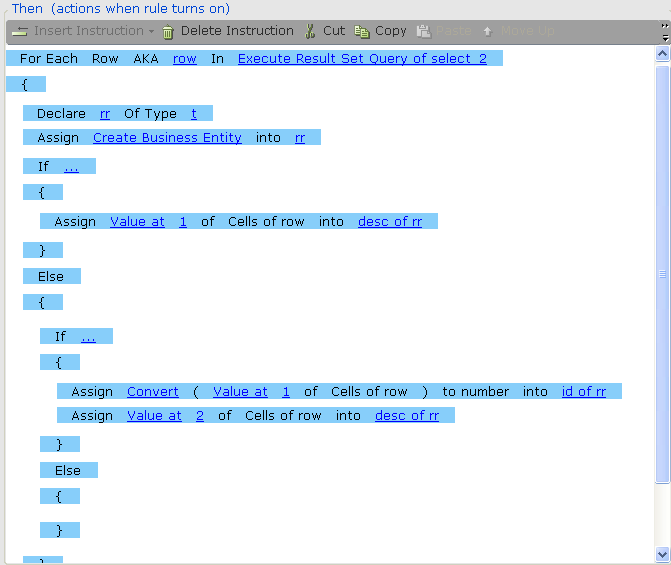
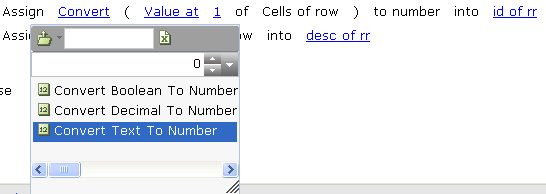
If you want to use a cell's value as a number, you must first convert it from a string to a number:
Fetch RTServer Data to DataTable: This function returns the query result from the RT Server database to the datatable. The supported datatype in DataTable are boolean, datetime, decimal, number, and string. Before you invoke this function, publish the associated solution in the RT Server. No parameter is required to invoke this function.
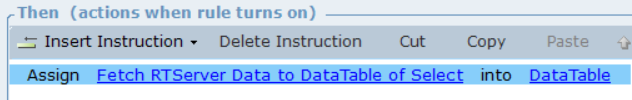
Load: This function loads query results into a business entity instance or list of instances. Refer to the To use a local database table in an Action Editor procedure for details about how to use this function. This function is equivalent to using the Load for Update function described there.
Let's look at an example of how to use the Load function in Asynchronous mode. Let's assume you have a rule that when triggered, invokes the Load function. After the function is triggered, the system waits for the server to respond. In this situation, how do you know that the server has responded and that the business entity was indeed updated? In this case, you have an asynchronous situation where you need to use an event to know when the server really replied with the result of the command.
If a rule synchronously invoked the query or the query was invoked using one of the available functions in synchronous mode (Execute Non Query, Execute Result Set Query, Load), the event tells you that the function was invoked but does not indicate the result of the command.
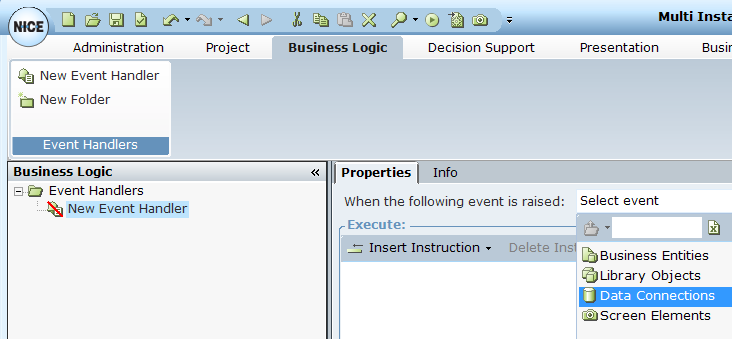
In this case, define an event handler to specify what action to take when the Load function is triggered.
First, specify that the event applies to a data connection:
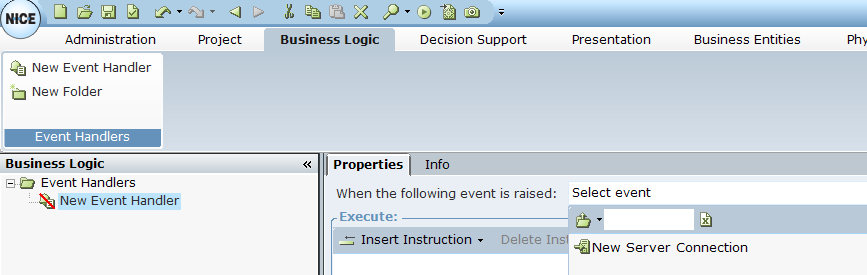
Then, specify that the event is triggered when a new server connection is executed:
Next, specify what action should occur when the event is triggered:
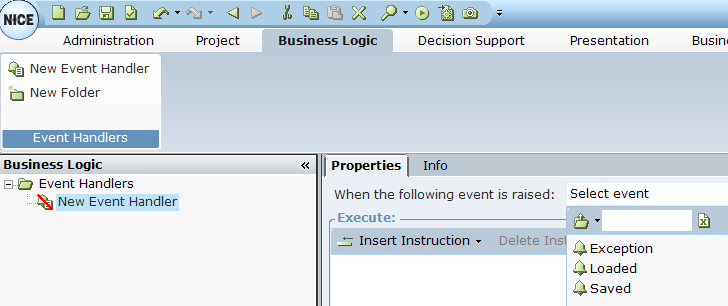
The available actions are:
Exception: An exception occurred (see Defining a Database Exception for details).
Loaded: The table was loaded into the business entities.
Saved: The Update function was invoked (see above for details).
