Process Path Discovery
Desktop Analytics' Process Path Discovery feature provides a strong analytical tool for discovering the actual process execution methods, in terms of applications and process tasks, used by call center or back office employees to accomplish their business processes. To accomplish a process, each employee may actually use slightly different methods, such as different applications in a different order, or performing process tasks in a different order.
Because processes have a success measure that represents the business goal, each process performed (process instance) has a measure value that represents that process instance’s success in achieving the business need.
The Process Path Discovery utilizes the Success Measure associated with a process to determine the overall measure value of a process instance.
For the purpose of path discovery, non-active time on the client is considered only when it reaches a duration threshold (meaning, the time was very long). Non-active time on the client includes idle time, hold time and locked time, as follows:
Idle time: The time when no mouse or keyboard action is detected on the client for longer than a specified threshold.
Hold time: The time that begins after a process starts, but before the first task starts, or the time between tasks.
All States, Process on Hold, Process Active , IDLE and LOCKED are separated one from the other. In other words, the states are not overlapped.
Locked time: The time when the client computer is in a locked state (by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del and then locking the computer).
This concept is illustrated in the following figure:
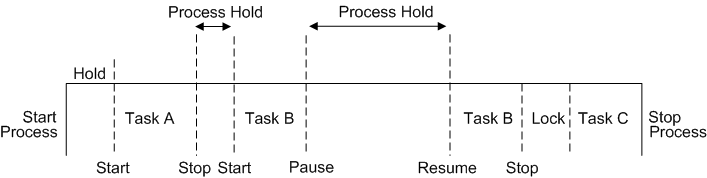
A threshold can be defined for each non-active time (idle, hold, locked). Values below these thresholds are ignored, in order to eliminate unnecessary noise. Idle, hold and lock time settings are configured in the System Settings window.
For details about configuring the settings described in this section, see the Real-time Server > Server branch in the System Settings window, which is described in the System Administration Guide.
