Service Delivery in Agile Best Practices
APA, also known as RTS, is a highly customizable technology product. The Agile methodology has an invaluable role to play in developing attended automations – combining technology with methodology.
Building attended automations requires continuous user feedback and interaction, which is fundamental to Agile. Key reasons to use Agile when developing attended automations, are rapid development, higher quality, and speedier value realization.
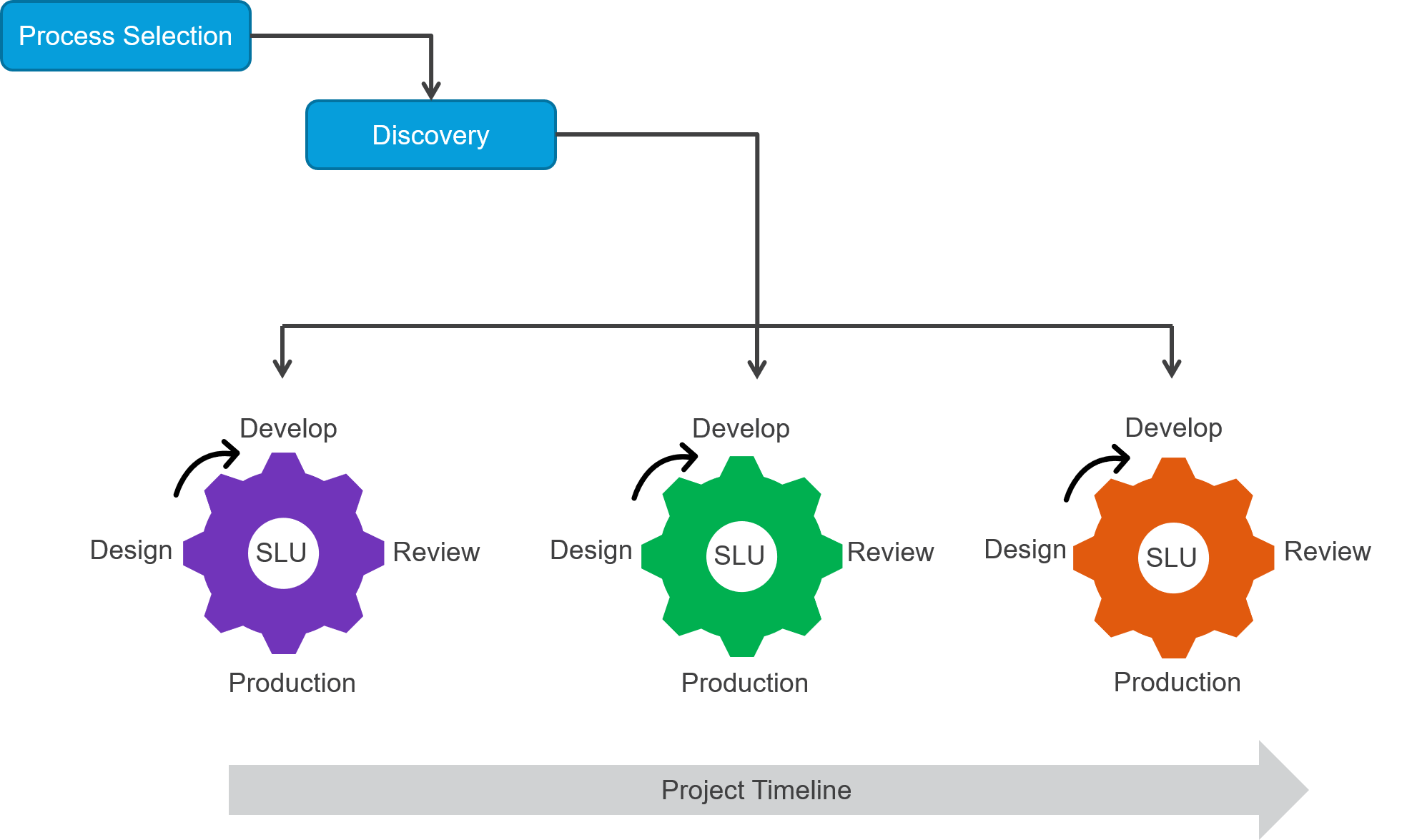
Discovery
The team sits together and reviews the process that needs to be automated. Face-to-face is best but when working remotely, video conferencing is recommended. If the teams work remotely, they should all be in a similar time zone in order to collaborate and retain agility.
The delivery team members jointly responsible for the success of the project. The developer must ask for whatever they need in order to start the development.
At the end of the planning arrange a short recap by the developer in order to ensure team alignment.
Construct the robotic automation process from the manual process.
The SME Process Owner presents the manual process. The Automation Business Analyst adjusts the manual steps to encapsulate robot capabilities, and where possible, reduce the number of highly complex steps in the process. For example, reading from Excel versus reading from an HTML table, or tree robot navigation versus right-click menu.
Close collaboration between the Process Owner, Automation Business Analyst, and the Automation Developer is crucial. Additional team members may be added to the Agile team, for example, Technical Lead and Agile Coach.
Close collaboration means that all the team members should be available to each other almost 100% for the first few days at the start of the project. In addition, these resources must be available to answer developer questions as soon as possible. It is recommended to assign a process owner or business analyst on-call, to make sure there is a resource available when needed. This helps streamline the development process, as issues can be dealt with as soon as they come up.
Identify Small Logical Units.
The Agile delivery team breaks the process into deliverable buckets called Small Logical Units (SLUs). An SLU needs to have meaningful business functionality. Set the priority on the SLUs and make the necessary effort estimations.
There is no requirement to have a minimum or maximum number of steps in an SLU. This helps to ensure function reusability. For example, a minimal SLU may be a button click or a value assignment, and at the maximum, the full process in a small project.
Typical meaningful business functionally:
-
Search customer
-
Login or logout to an application
-
Add/remove customer
-
Error handling mechanism

Identify the most used SLU.
This allows you to present a demo early on that illustrates the value of the automation, ensuring that you are illustrating the ROI to management.
Do this by looking for:
-
Simple functionally (low number of steps, easy to implement).
-
Certain functionally that most likely won’t change during the process development (login, logout).
-
Standalone functionally, no dependencies, clear output and input (add/remove).
-
Customer acceptance
Identify the main workflow from the set of SLUs.
Define a few test cases to be created by the customer.
Design
Design is completed as required and only when needed. There is no separate design phase. Draw the process and sub-processes on a board. Treat this drawing as something that can be changed during development.
Use sticky notes to describe the development work items, if needed, and only for the most immediate SLUs. Sticky notes may be written up in advance, for example, in the discovery phase and may also be adjusted during the development.
The sticky notes approach enables everyone to see what is being worked on, what is complete, what is in progress, and what remains to be started. This provides transparency to the team who can see, at a glance, whether they are on track to meet their Sprint goal, have too much work in progress, or are blocked on one or more stories.
Start the design with the most common SLU to allow immediate development execution of the process.
Aggregate SLUs into sprints to generate meaningful functional logic.
Continue design of the next best common SLUs to generate a SLU backlog for development.
Create the main flow by connecting designed SLUs/Sprints. This indicates the readiness of the designed SLUs and, in parallel, is a key element that can be used to improve the quality of the design of the remaining SLUs. It is possible that creating the main flow will result in the redesign of existing SLUs.
Verify the creation of test cases.
Backlog Management
The design progress is faster than the development process and the BA will therefore create the SLUs backlog.
Each SLU within the backlog includes:
-
Effort estimation
-
Priority
-
Dependencies between various SLUs and the main flows (if exists)
-
Complexity
-
Technology (for example: Java, IE, Terminal, Windows application)
The SLU backlog is organized according to the business needs.
Development
Aim to start development on the 1st day.
The entire team must be focused on removing obstacles to enable the developers to complete their development. The team removes uncertainty caused by lack of knowledge. This is how risk management is addressed in Agile.
The process drawn in the planning can be changed by the developers and the team to best describe reality.
Testing is embedded within the development and this means that when the development is done it is already tested.
When a sub-process is ready, a short demo is presented in order to get feedback.
A development phase of a sub-process as decided above, is being repeated to the rest of the sub-process until full process developed
Retrospectives
A retrospective is a short meeting where one thing is identified to keep and make a standard, and one thing is identified to fix in the next development iteration.
When the entire process ends the team does a thorough retrospective meeting. This obligates all employees with the development and management team.
